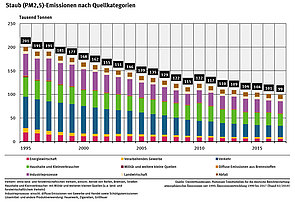
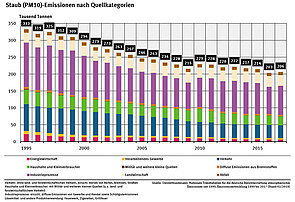
Dust emissions Germany
By using dedusting plant in industry and energy sector, the dust content could be forced back since the 80s.
Source: Umweltbundesamt, Nationale Trendtabellen für die deutsche Berichterstattung atmosphärischer Emissionen, Emissionsentwicklung 1990-2010 (Endstand 15. April 2012)
Industrial Dusts
In many industrial processes, air is used as a working medium and its composition is altered or it picks up contaminants during the process, e.g., in the pneumatic conveying of bulk material.
Many kinds of dust are hazardous to health, toxic or explosive and harmful to both people and the environment. Should the air later be released from the process back out into the atmosphere, any contaminants must be removed from the air. Other gases, such as nitrogen, are often used as a working medium. Contaminants have to be filtered from these gases as well, either to be able to feed the clean gas back into the process or to recover valuable products.
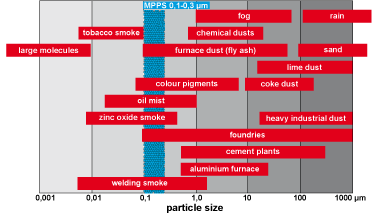
The dust particles in dust-laden gas flows generally range from 0.1 to 1,000 µm in size.
MPPS: Most penetrating particle size.
Particle range around 0.1 to 0.3 µm. In this range, particles are separated most severly (separating minium). This is independent of filter material and filter product. Because of this, test aerosols for highefficiency particulate air filter are located in this particle range.
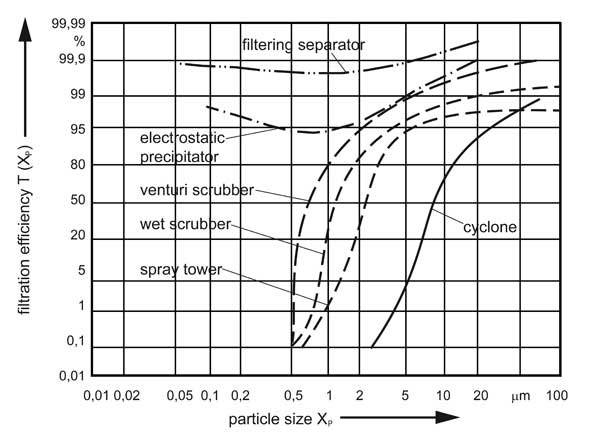
Technical processes for dust removal
Dust particles are separated from gas using various dust removal processes and dust separators.
- Gravity separators (e.g., settling chamber)
- Centrifugal separators (e.g., cyclone)
- Wet scrubbers (rotary scrubber, high-performance scrubber, etc.)
- Electric separators (electrostatic precipitator)
- Filtration separators (fabric filter, cartridge filter)
Fig.: Abscheidegrade unterschiedlicher Entstaubungsverfahren. Die Abscheidegrade stehen immer in Abhängigkeit zur Korngröße.
(Bank, Matthias Dr., Basiswissen Umwelttechnik, 2006)
Principles of surface filtration
Mechanisms underlying particle transport from the gas phase to the collectors basically involve inertial forces, diffusion-related forces and electrostatic forces. Furthermore, the interception, i.e. impaction solely due to the spatial extent of the particles, plays a role. Besides impaction, the adhesion of the particles to the collectors is critical to particle collection.
For a detailed description of the particle collection mechanisms involved, reference is made to VDI 3677 Part 2.
With increasing dust entrapment, particle interaction increases so that separation can no longer be satisfactorily described by the particle/single collector system; dendritic growth and bridging occur. As further dust is deposited, collection occurs almost exclusively on the surface of the filter medium in the filter cake building up as a result of the interception. The collection efficiency of this filter type improves significantly over time, i.e. as a function of the particle mass collected per unit area of the filter medium.
Source: VDI 3677, Part 1, Filtering separators, Surface filters
Sieve effect |  | Barrier effect |  |
Inertial effect |  | Diffusion effect |  |